
What is experiential learning?
The Center of Education and Innovation is committed to supporting the use of experiential learning at The University of Hong Kong Science and Technology. Experiential learning is a natural and powerful learning tool that helps foster problem-solving, critical thinking, and growth. Watch the video below to understand how this is a natural learning process that each of us has utilized from a young age.

Are you interested in understanding how to design an experiential course or TLIP project? This short guide is intended to help support your understanding of experiential learning and how to put it into practice in higher education.
How is experiential learning different from traditional practice?
Experiential learning is different from traditional modes of learning in its learning outcomes, goals, and the roles that students and teachers assume.

There may be failures or challenges along the way because goals and outcomes are flexible. This is a part of experiential learning - the process (including failure or challenges) is as important as the learning outcome.
How do I transition from ‘instructor’ to ‘facilitator’?
Being a facilitator takes careful consideration, planning, and practice. It can sometimes be difficult to ‘part ways’ with our instinct to teach traditionally. Here are some ideas to help you on your way to becoming a facilitator:
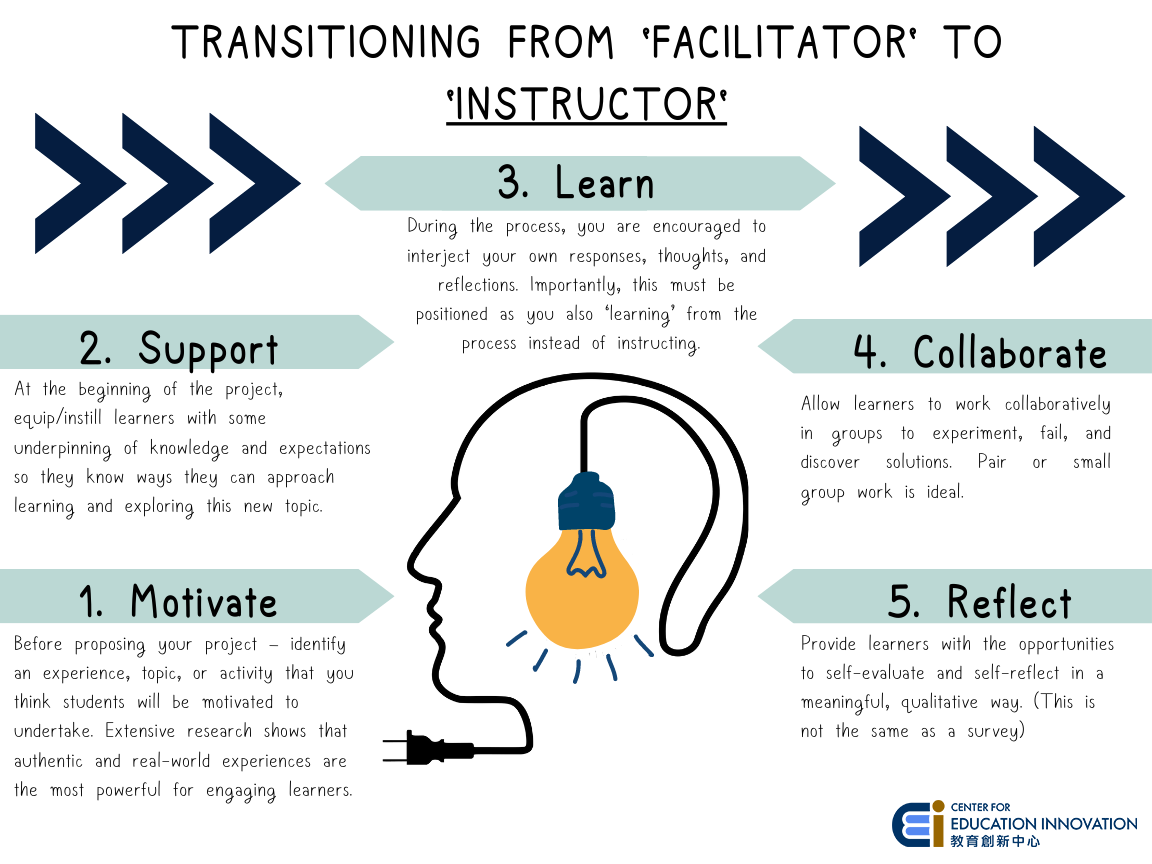
As a facilitator, you will be helping learners become ‘meaning-makers’ instead of knowledge recipients.
How do I design an experiential learning project?
David A. Kolb, a noted educational theorist, proposed a framework for how this works in practice. His framework can help you better understand the pivotal stages of experiential learning.


Take these stages into consideration when designing your projects. Click here for in-depth information about this experiential learning cycle.
Experiential Learning in Practice
For your learning course or project to be recognized as ‘experiential’ at HKUST, it must contain:

Authentic and real-life experiences for students to engage in intellectually, emotionally, socially, and/or socially

Opportunities for students to pose questions, investigate, experiment, take initiative, make decisions, and be accountable for the results

A reflective process that leads to analysis, critical thinking and synthesis

A well-designed learning experience that allows students to learn from natural consequences, mistakes and successes
Sometimes it can be difficult to discern between experiential learning and traditional learning, especially as the latter can still use real-life or authentic experiences. We invite you to take this quick quiz to see if you can identify which projects are (or are not!) experiential.
Checklist
Experiential learning is a powerful method for fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovation in learners. Would you like to propose a TLIP project or university course that uses experiential learning? Ask yourself the questions below before submitting your proposal:

Additional Resources
Want to learn more about experiential learning? Below are some useful resources:Association for Experiential Education
Experiential Learning in Higher Education (International Journal of Advance Research and Innovation)
An Instructional Guide (Northern Illinois University)
Experiential learning: Transforming theory into practice (Medical Teacher)

